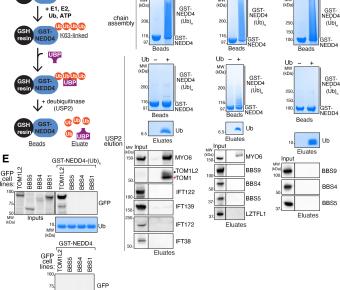
The ancestral ESCRT protein TOM1L2 selects ubiquitinated cargoes for retrieval from cilia.
April 24, 2023
Many G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) reside within cilia of mammalian cells and must undergo regulated exit from cilia for the appropriate transduction of signals such as hedgehog morphogens. Lysine 63-linked ubiquitin (UbK63) chains mark GPCRs for regulated removal from cilia, but the... Genetics of myocardial interstitial fibrosis in the human heart and association with disease
April 20, 2023
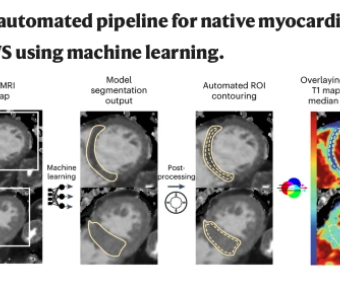
Myocardial interstitial fibrosis is associated with cardiovascular disease and adverse prognosis. Here, to investigate the biological pathways that underlie fibrosis in the human heart, we developed a machine learning model to measure native myocardial T1 time, a marker of myocardial fibrosis, in... The next big questions in cancer research
April 13, 2023
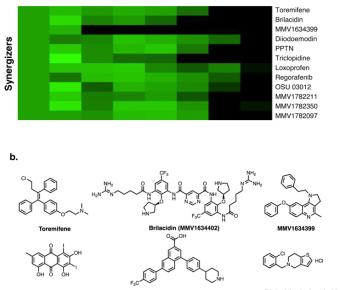
Our understanding of tumorigenesis and cancer progression as well as clinical therapies for different cancer types have evolved dramatically in recent years. However, even with this progress, there are big challenges for scientists and oncologists to tackle, ranging from unpacking the molecular and... A host defense peptide mimetic, brilacidin, potentiates caspofungin antifungal activity against human pathogenic fungi.
April 12, 2023
Fungal infections cause more than 1.5 million deaths a year. Due to emerging antifungal drug resistance, novel strategies are urgently needed to combat life-threatening fungal diseases. Here, we identify the host defense peptide mimetic, brilacidin (BRI) as a synergizer with caspofungin (CAS)... Aberrant activation of TCL1A promotes stem cell expansion in clonal haematopoiesis
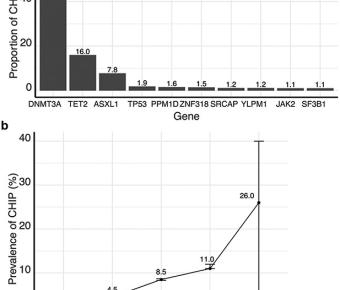
April 01, 2023
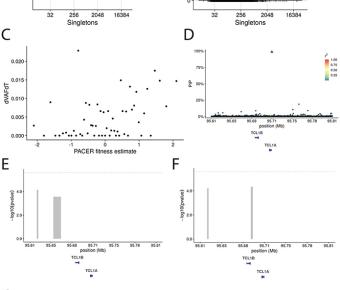
Mutations in a diverse set of driver genes increase the fitness of haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), leading to clonal haematopoiesis1. These lesions are precursors for blood cancers2-6, but the basis of their fitness advantage remains largely unknown, partly owing to a paucity of large cohorts in... Clonal haematopoiesis and risk of chronic liver disease.
April 01, 2023
Chronic liver disease is a major public health burden worldwide1. Although different aetiologies and mechanisms of liver injury exist, progression of chronic liver disease follows a common pathway of liver inflammation, injury and fibrosis2. Adjusting for common variant polygenic scores improves yield in rare variant association analyses
April 01, 2023
With the emergence of large-scale sequencing data, methods for improving power in rare variant association tests are needed. Here we show that adjusting for common variant polygenic scores improves yield in gene-based rare variant association tests across 65 quantitative traits in the UK Biobank (... Clinical and genetic associations of deep learning-derived cardiac magnetic resonance-based left ventricular mass.
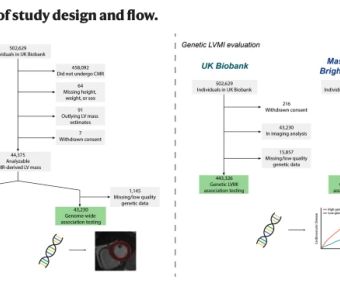
March 21, 2023
Left ventricular mass is a risk marker for cardiovascular events, and may indicate an underlying cardiomyopathy. Cardiac magnetic resonance is the gold-standard for left ventricular mass estimation, but is challenging to obtain at scale. Here, we use deep learning to enable genome-wide association... ATM-SPARK: A GFP phase separation–based activity reporter of ATM
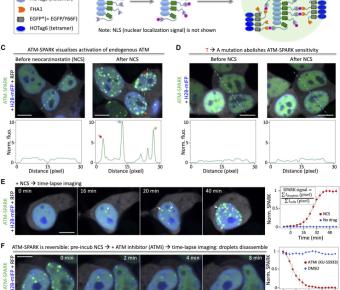
March 01, 2023
The kinase ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) plays a key role in the DNA damage response (DDR). It is thus essential to visualize spatiotemporal dynamics of ATM activity during DDR. Here, we designed a robust ATM activity reporter based on phosphorylation-inducible green fluorescent protein phase... Graded mesoderm assembly governs cell fate and morphogenesis of the early mammalian heart.
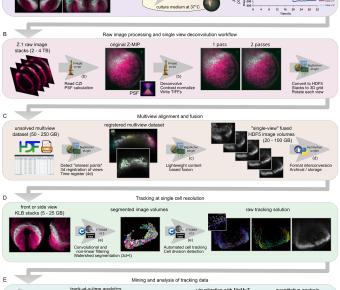
February 02, 2023
Using four-dimensional whole-embryo light sheet imaging with improved and accessible computational tools, we longitudinally reconstruct early murine cardiac development at single-cell resolution. Nascent mesoderm progenitors form opposing density and motility gradients, converting the temporal...