Clonal haematopoiesis and risk of chronic liver disease.
April 01, 2023
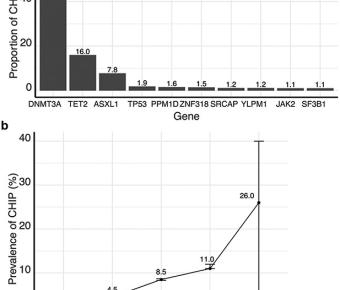
Chronic liver disease is a major public health burden worldwide1. Although different aetiologies and mechanisms of liver injury exist, progression of chronic liver disease follows a common pathway of liver inflammation, injury and fibrosis2. Aberrant activation of TCL1A promotes stem cell expansion in clonal haematopoiesis
April 01, 2023
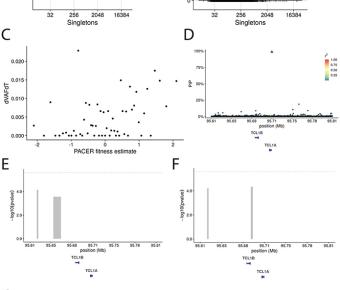
Mutations in a diverse set of driver genes increase the fitness of haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), leading to clonal haematopoiesis1. These lesions are precursors for blood cancers2-6, but the basis of their fitness advantage remains largely unknown, partly owing to a paucity of large cohorts in... Clinical and genetic associations of deep learning-derived cardiac magnetic resonance-based left ventricular mass.
March 21, 2023
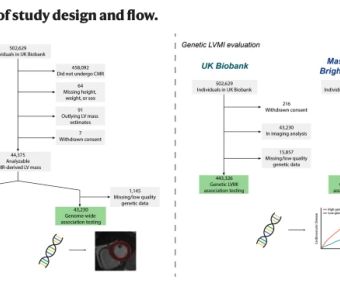
Left ventricular mass is a risk marker for cardiovascular events, and may indicate an underlying cardiomyopathy. Cardiac magnetic resonance is the gold-standard for left ventricular mass estimation, but is challenging to obtain at scale. Here, we use deep learning to enable genome-wide association... ATM-SPARK: A GFP phase separation–based activity reporter of ATM
March 01, 2023
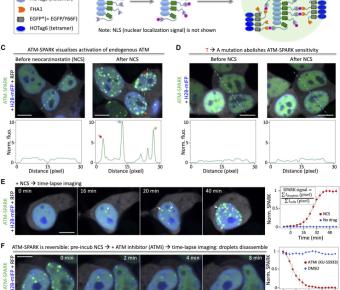
The kinase ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) plays a key role in the DNA damage response (DDR). It is thus essential to visualize spatiotemporal dynamics of ATM activity during DDR. Here, we designed a robust ATM activity reporter based on phosphorylation-inducible green fluorescent protein phase... Graded mesoderm assembly governs cell fate and morphogenesis of the early mammalian heart.
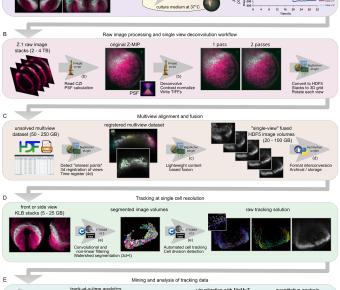
February 02, 2023
Using four-dimensional whole-embryo light sheet imaging with improved and accessible computational tools, we longitudinally reconstruct early murine cardiac development at single-cell resolution. Nascent mesoderm progenitors form opposing density and motility gradients, converting the temporal... Smarcd3 is an epigenetic modulator of the metabolic landscape in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
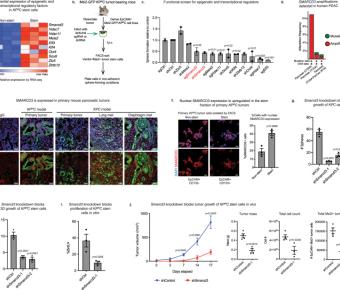
January 18, 2023
Pancreatic cancer is characterized by extensive resistance to conventional therapies, making clinical management a challenge. Here we map the epigenetic dependencies of cancer stem cells, cells that preferentially evade therapy and drive progression, and identify SWI/SNF complex member SMARCD3 as a... TP53-mediated clonal hematopoiesis confers increased risk for incident atherosclerotic disease.
January 16, 2023
Somatic mutations in blood indicative of clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) are associated with an increased risk of hematologic malignancy, coronary artery disease, and all-cause mortality. Here we analyze the relation between CHIP status and incident peripheral artery disease... Nature – Pump, rest, leak, repeat by Dr. Michael Grabe
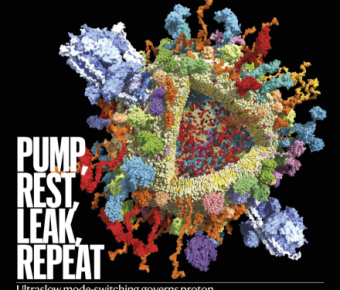
November 23, 2022
The cover illustration shows vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases, large blue structures) on a synaptic vesicle from a nerve cell in the mammalian brain. V-ATPases pump protons across cellular membranes, and in neurons this process is essential for loading neurotransmitters into... Dr. Pui Kwok elected to World Academy of Sciences
November 02, 2021
Dr. Pui Kwok has been elected to the World Academy of Sciences (TWAS) for the advancement of scientific in developing countries, a UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) honor society that is like the US National Academy of Science for the developing countries. Adrenergic-Thyroid Hormone Interactions Drive Postnatal Thermogenesis and Loss of Mammalian Heart Regenerative Capacity
September 20, 2021
Why can’t adult human hearts regenerate after injury like a heart attack? The Huang lab recently presented findings in Circulation to support that loss of cardiac regenerative capacity may be a tradeoff for us to be warm-blooded, and now identified the second major thermogenic pathway that is...